Share the post "Billions Spent on Somalia Security: Why Has Al-Shabaab Not Been Defeated?"
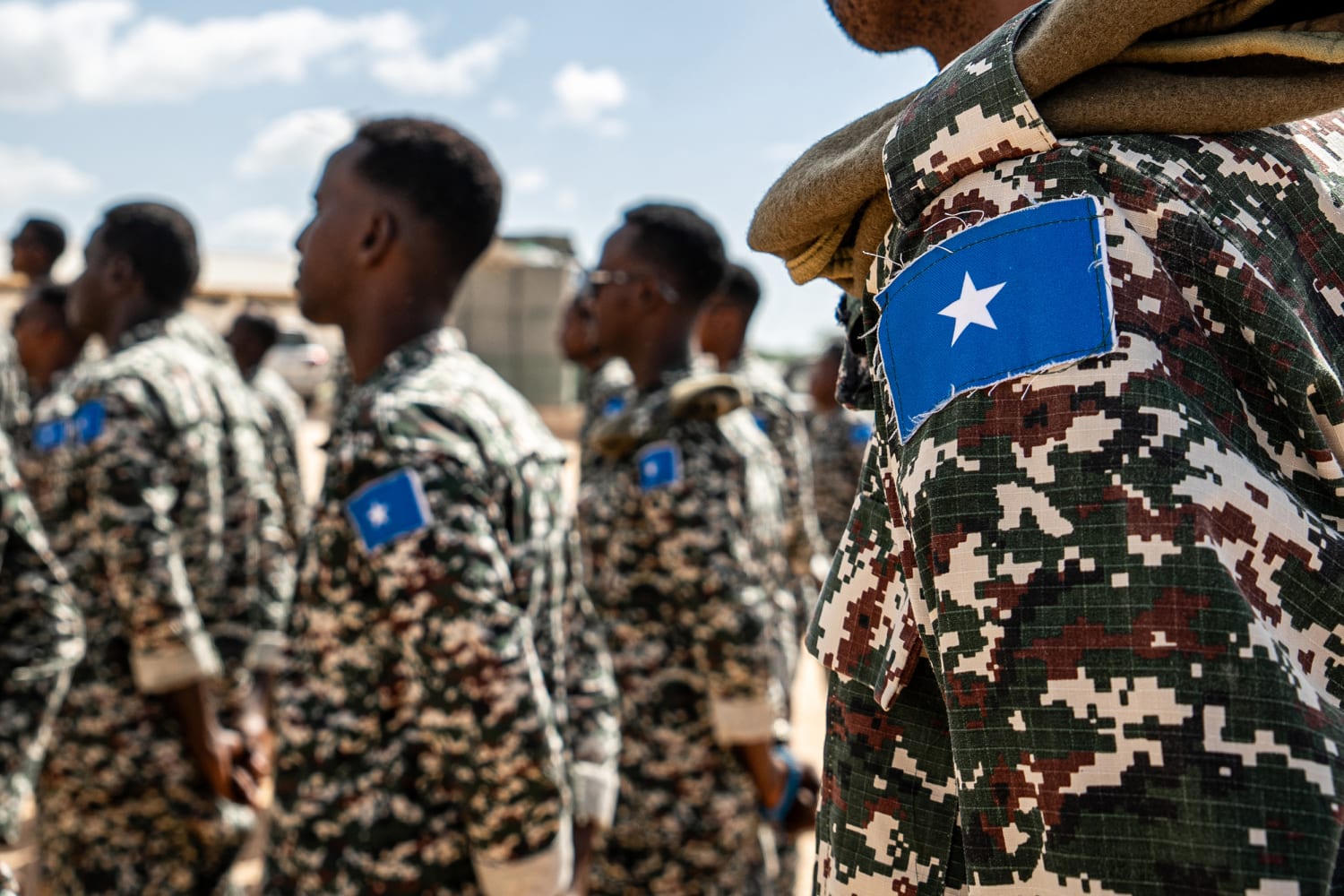
Over the past 19 years, the United States and European countries have collectively spent billions of dollars on security assistance for Somalia. These funds have primarily supported the Somali National Army (SNA), African Union peacekeeping missions (AMISOM, ATMIS & AUSSOM), counterterrorism operations, and capacity-building programs aimed at stabilising the country…
How Much Has Been Spent?
While exact figures vary, estimates suggest that:
•The United States alone has provided over $3 billion in military and security aid to Somalia since 2006, funding counterterrorism operations, drone strikes, and training for Somali forces. (Source: U.S. Department of Defense, Congressional Research Service)
•The European Union has contributed over €2 billion ($2.2 billion) toward AMISOM and later ATMIS operations, paying salaries for African peacekeepers and providing logistical support. (Source: European External Action Service, EUCAP Somalia)
•Other international partners, including the United Kingdom, Turkey, and Gulf states, have also provided military assistance, training, and weapons.
Despite this significant investment, Al-Shabaab remains a powerful insurgent force, continuing to launch deadly attacks across Somalia, including in the capital, Mogadishu.
Why Has Al-Shabaab Not Been Defeated?
1.Corruption and Mismanagement
•Reports indicate that a large portion of foreign aid meant for security forces is lost due to corruption, mismanagement, and lack of accountability. Somali military personnel have often gone unpaid, and weapons have allegedly fallen into the hands of Al-Shabaab. (Source: Transparency International, UN Monitoring Group on Somalia)
2.Weak and Divided Somali Government
•Political instability, clan rivalries, and lack of coordination between federal and regional forces have weakened counterterrorism efforts. Different factions within the Somali government often work at odds with each other, preventing a unified strategy against Al-Shabaab. (Source: International Crisis Group, Somalia Affairs Institute)
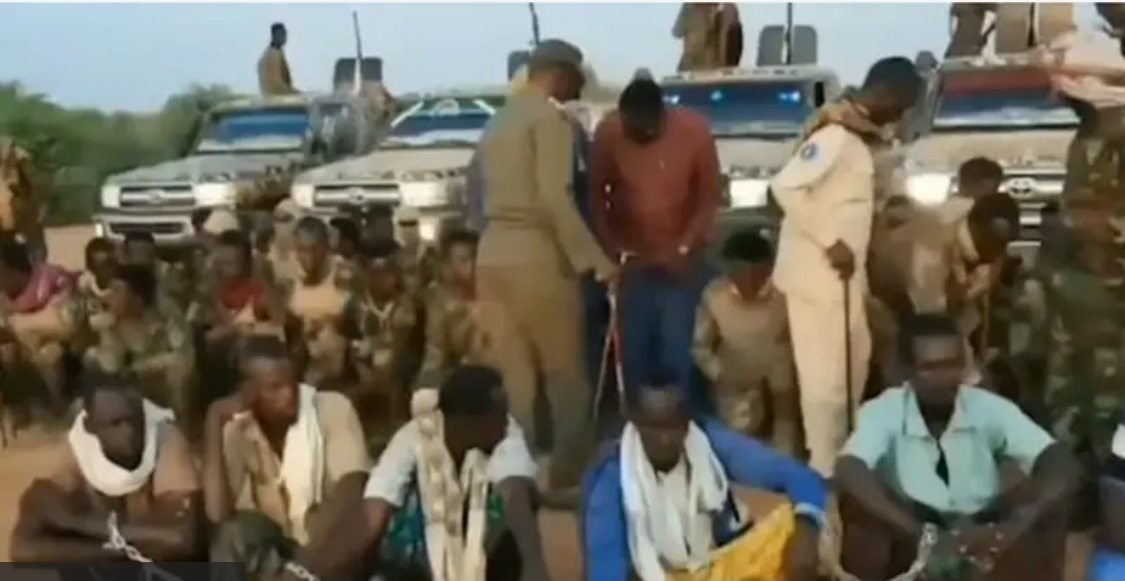
3.Al-Shabaab has adapted, using guerrilla warfare, extortion, and intelligence networks to remain deeply embedded in local communities.
4.Ineffective International Strategies
•The reliance on foreign peacekeeping forces (AMISOM/ATMIS) rather than a fully independent Somali army has created a dependency problem. The planned withdrawal of ATMIS forces by 2024 raises concerns that Somali forces may not be ready to handle security alone. (Source: African Union, UN Security Council reports)
5.Donor Fatigue and Shifting Priorities
.With ongoing global crises (Ukraine war, Middle East conflicts), international donors may be losing interest in funding Somali security. There are signs of reduced financial commitments from some Western nations, as other geopolitical priorities take focus. (Source: Foreign Policy, US State Department briefings)
Is the World Losing Interest in Somalia?
While Western support remains, it is clear that donor fatigue is setting in. If Somalia does not take stronger measures to combat corruption, improve governance, and strengthen its military, external funding could decline, potentially leaving Somalia even more vulnerable to Al-Shabaab’s resurgence.