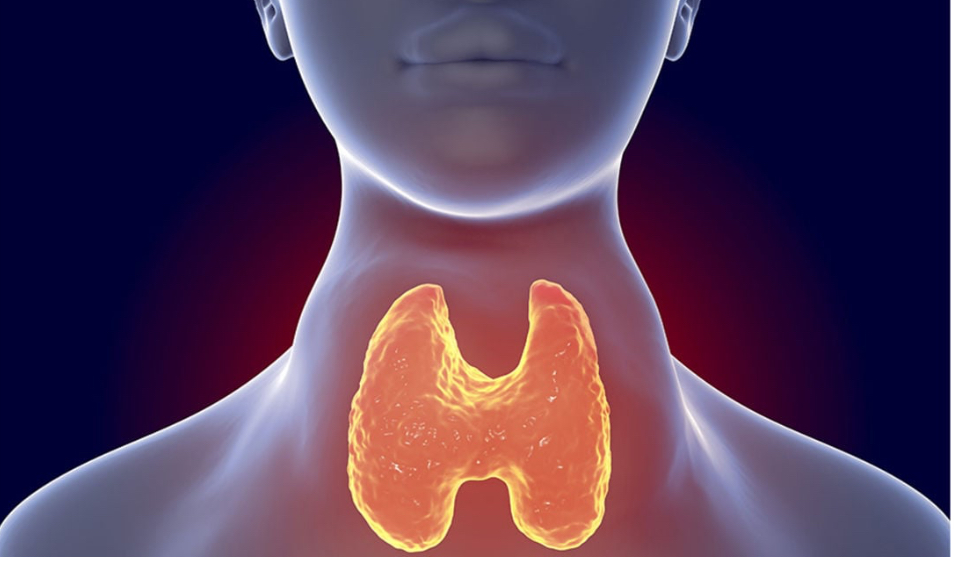
Hyperthyroidism, also called overactive thyroid, is a condition where your thyroid makes and releases high levels of thyroid hormone. This condition can make your metabolism speed up. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include a rapid heartbeat, weight loss, increased appetite and anxiety. Hyperthyroidism can be treated with antithyroid drugs, radioactive iodine, beta blockers and surgery…
What is hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which your thyroid creates and releases more hormones than you need. This is also called overactive thyroid. The main hormones your thyroid makes include triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), Hyperthyroidism can affect your entire body and is a condition that needs to be treated by a healthcare provider.
What is the difference between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are medical conditions that both have to do with the amount of thyroid hormone your thyroid makes and releases — the difference is how much, Picture something related to the word “hyper.” Most likely, you just thought of something fast or full of a lot of energy. When you have hyperthyroidism, your thyroid is overactive and produces and releases too much thyroid hormone.
In the medical world, the prefix “hypo-” means “low” or “not enough.” When you have hypothyroidism, your thyroid is under-active and doesn’t make and release enough thyroid hormone that your body needs.
Who gets hyperthyroidism?
Anyone can have hyperthyroidism, but it’s more common in females.
How common is hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is relatively rare. Approximately 1% of people in the United States have hyperthyroidism.
What are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
There are many symptoms of hyperthyroidism, and they can impact your entire body. You may experience some of these symptoms and not others, or many of them at the same time. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism can include:
- Rapid heartbeat (palpitations).
- Feeling shaky and/or nervous.
- Weight loss.
- Increased appetite.
- Diarrhea and more frequent bowel movements.
- Vision changes.
- Thin, warm and moist skin.
- Menstrual changes.
- Intolerance to heat and excessive sweating.
- Sleep issues.
- Swelling and enlargement of the neck from an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter).
- Hair loss and change in hair texture (brittle).
- Bulging of the eyes (seen with Graves’ disease).
- Muscle weakness.